Sensor Diagnostics Demo
This tutorial walks through the sensor_diagnostics demo — a lightweight demonstration of ros2_medkit’s monitoring, configuration, and fault detection capabilities.
Overview
The sensor diagnostics demo showcases ros2_medkit with simulated sensor nodes:
LiDAR Simulator — 2D laser scanner with fault injection
Camera Simulator — RGB camera with noise and brightness control
IMU Simulator — 9-DOF inertial measurement unit
GPS Simulator — GPS receiver with position drift
Anomaly Detector — Monitors sensor data for faults
Key Features:
Runs anywhere — no Gazebo, no GPU required
Fast startup — seconds vs minutes
Docker-based deployment with web UI included
Dual fault reporting paths (legacy diagnostics + modern direct)
Runtime fault injection via REST API
Prerequisites
Docker and Docker Compose installed
Git (to clone the demo repository)
Starting the Demo
Clone the demo repository and run the startup script:
git clone https://github.com/selfpatch/selfpatch_demos.git
cd selfpatch_demos/demos/sensor_diagnostics
# Start the demo (daemon mode)
./run-demo.sh
Terminal showing demo services starting up.
The script will build and start Docker containers with:
ros2_medkit gateway (REST API on port 8080)
sovd_web_ui (Web interface on port 3000)
Simulated sensor nodes (lidar, camera, imu, gps)
Anomaly detector for fault monitoring
Diagnostic bridge for legacy fault reporting
Startup Options:
./run-demo.sh --attached # Run in foreground with logs
./run-demo.sh --update # Pull latest images
./run-demo.sh --no-cache # Build without cache
Exploring the Demo
Open the web UI at http://localhost:3000 and connect to the gateway at http://localhost:8080 and api/v1
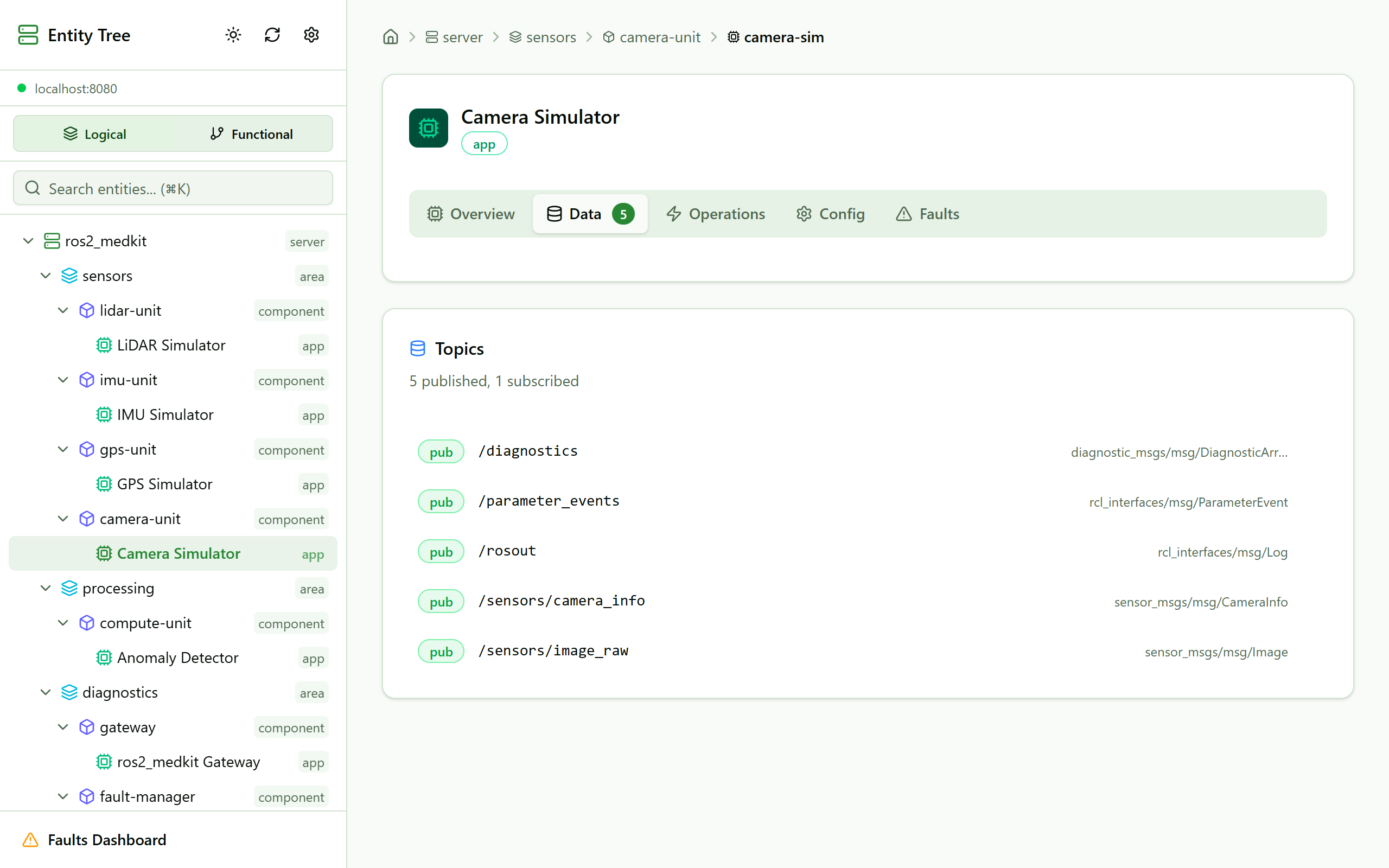
Web UI showing sensor demo entity hierarchy.
The demo exposes entities organized by namespace:
/sensors— Sensor simulator nodes (lidar, camera, imu, gps)/processing— Anomaly detector/bridge— Diagnostic bridge/diagnostics— ros2_medkit gateway
Interactive API exploration:
# Run the interactive check script
./check-demo.sh
Reading Sensor Data
Navigate to a sensor app in the web UI and explore the data folder to see published topics.
Query sensor data via REST API:
# Get LiDAR scan
curl http://localhost:8080/api/v1/apps/lidar-sim/data/scan | jq '.ranges[:5]'
# Get IMU data
curl http://localhost:8080/api/v1/apps/imu-sim/data/imu | jq '.linear_acceleration'
# Get GPS fix
curl http://localhost:8080/api/v1/apps/gps-sim/data/fix | jq '{lat: .latitude, lon: .longitude}'
# Get camera image info
curl http://localhost:8080/api/v1/apps/camera-sim/data/image | jq '{width, height, encoding}'
Managing Configurations
Click on the configurations folder in the web UI to see ROS 2 parameters for each sensor.
View and modify sensor parameters:
# List all LiDAR configurations
curl http://localhost:8080/api/v1/apps/lidar-sim/configurations | jq
# Get specific parameter
curl http://localhost:8080/api/v1/apps/lidar-sim/configurations/noise_stddev | jq
# Change scan rate
curl -X PUT http://localhost:8080/api/v1/apps/lidar-sim/configurations/scan_rate \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"value": 20.0}'
Key Parameters:
scan_rate/rate— Publishing frequency (Hz)noise_stddev/noise_level— Sensor noise magnitudedrift_rate— Gradual sensor driftfailure_probability— Probability of sensor timeoutinject_nan/inject_black_frames— Fault injection flags
Fault Injection
The demo starts with normal sensor operation (no faults). You can inject faults at runtime using provided scripts:
Available fault injection scripts:
# Inject high noise (triggers legacy diagnostics path)
./inject-noise.sh
# Inject sensor timeouts
./inject-failure.sh
# Inject NaN values in sensor data
./inject-nan.sh
# Inject sensor drift
./inject-drift.sh
# Restore normal operation
./restore-normal.sh
View active faults:
# List all system faults
curl http://localhost:8080/api/v1/faults
# Get faults for specific sensor
curl http://localhost:8080/api/v1/apps/lidar-sim/faults
Manual fault injection via API:
You can also inject faults by setting parameters directly:
# Increase noise level
curl -X PUT http://localhost:8080/api/v1/apps/lidar-sim/configurations/noise_stddev \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"value": 0.5}'
# Enable NaN injection
curl -X PUT http://localhost:8080/api/v1/apps/imu-sim/configurations/inject_nan \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"value": true}'
# Increase failure probability
curl -X PUT http://localhost:8080/api/v1/apps/gps-sim/configurations/failure_probability \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"value": 0.3}'
Stopping the Demo
To stop all services:
./stop-demo.sh
Or manually:
docker compose down
Architecture
The demo implements the following architecture:
Sensor Diagnostics Demo
├── /sensors # Simulated sensor nodes
│ ├── lidar_sim # 2D LiDAR (Legacy path)
│ ├── camera_sim # RGB camera (Legacy path)
│ ├── imu_sim # 9-DOF IMU (Modern path)
│ └── gps_sim # GPS receiver (Modern path)
├── /processing # Data processing
│ └── anomaly_detector # Fault detection
├── /bridge # Diagnostic conversion
│ └── diagnostic_bridge # /diagnostics → FaultManager
└── /diagnostics # Monitoring
└── ros2_medkit_gateway # REST API gateway
See Also
Getting Started — Basic gateway setup
REST API Reference — REST API reference
Fault Manager Configuration — Fault Manager configuration
TurtleBot3 Demo — TurtleBot3 simulation demo
selfpatch_demos — Demo repository